1. Achilles tendonitis
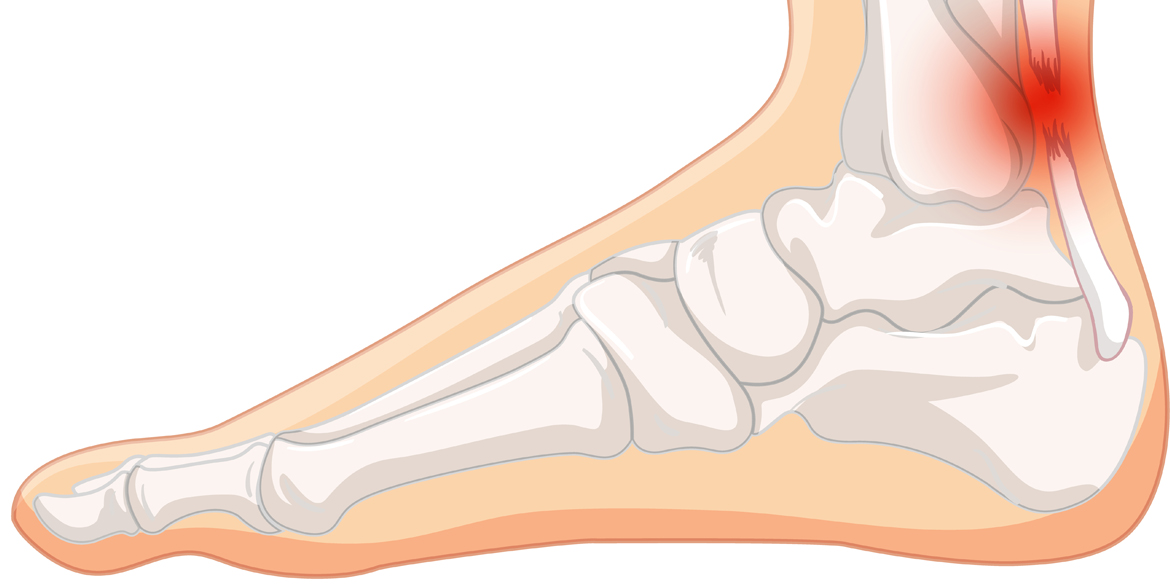
The Achilles tendon joins calf muscles (gastrocnemius and soleus) to the heel. If you have pain in the back of the leg close to heal area, then it may be Achilles tendon inflammation. There could be many reasons for this including improper footwear, running on hard surface especially without warming and stretching, prolonged standing, direct trauma, muscle weakness. Symptoms if this disease are local pain and tenderness, swelling, stiffness, morning pain, rigidity in the area. The tests which are helpful in diagnosing this disease are
Lateral X rays – helps in diagnosing calcification in the tendon, bony spurs etc
Ultrasound of the foot – gives information about tendon thickness, hyperaemia, tear etc.
MRI – Provides information about joint structures and in various planes.
Treatment includes
- Conservative management – Rest, NSAIDs, eccentric and tendon loading exercises.
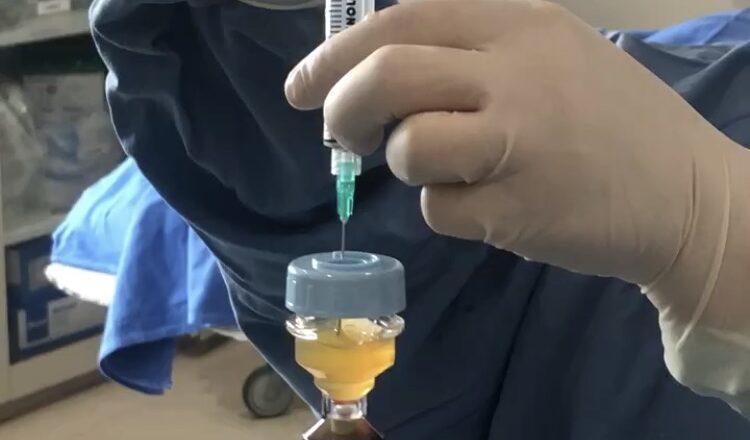
- Injections – Various options include Saline injection, PRP (Platelet rich plasma) helps by decreasing the hyperaemia, repair of the torn tendon.
- Surgery – If the tendon is completely ruptured, then surgery is needed for complete repair.
2. Morton’s neuroma
Pain in the forefoot along with sensation of swelling/knotted feeling in the ball of the foot. It happens due to rubbing of forefoot bones with each other and hence causing pressure over the nerves. This leads to the swelling of the nerves. It occurs usually between 3rd and 4th toes or 2nd and 3rd toes. Treatment includes supportive shoes, rest. In some cases, cortisone injection can help which is done under ultrasound guidance by the pain physicians. In severe cases surgery may be needed.
3. Plantar fasciitis
Pain in the heel or the arch of the foot . It is due to inflammation of the fascia ( fibrous tissues) which connects from heel to the base of the toes. It happens in the people who have flat foot, their job requires lot of standing and walking on the hard surfaces. Running without warming up can also contribute to the condition. Treatment includes
- Wearing Supportive shoes
- Intermittent icing
- Stretching exercises as taught during physical therapy or by the doctor
- Steroid Injection.
- PRP ( platelet rich plasma) therapy
- Surgery
4. Tarsal tunnel Syndrome
This is due to compression of the nerve named posterior tibial nerve or one of its branches within the compartment in the feet called tarsal tunnel. Different causes like trauma, ankle sprains, overweight, flat feet, bony spurs, arthritis. Risk factors include DM, hypothyroidism, gout. The predominant pain includes pain in the arch and planter foot, sharp shooting pain, numbness, tingling, pins, and needle like sensation, burning sensation. Electromyography helps in the diagnosis. Early treatment includes rest and anti-inflammatory medications.
Nerve release injection therapy à This procedure includes injection of medication around the nerve with the help of ultrasound guidance. It releases nerve compression and is helpful in the pain management. Prolotherapy (PRP, dextrose therapy) helps in repair and strengthening of injured structures.
Surgery à excision of neuroma, nerve release are few options depending on the cause can help in severe cases.
5. Bone Spurs/Heel Spurs
It is a bony overgrowth at the heel usually due to excess weight, overuse and ill-fitting shoes. This causes inflammation over the tissues and hence pain. The treatment is rest, application of intermittent ice at the affected area, proper fitting shoes, steroid injection and in some case surgery
6. Ankle joint arthritis
The arthritis is a term used for swelling and inflammation of the joint. And when this sets in, it causes the loss of cartilage which acts as a cushion inside the joint. The early symptoms of ankle arthritis are pain and swelling around the joint. Later there is decreased range of motion, joint stiffness and redness. The pain will be more at rest especially when you wake up in the morning. Diagnosis is usually made by physical exam, X rays and sometimes CT scan and MRI would be needed.
Treatment includes
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Steroid injections
- Brace for support
- Arch Support
- Exercises safe for arthritis
7. Neuropathy
Damage to the nerves causes symptoms like pain, numbness, burning sensation, pins and needle like sensation, sensitivity to touch, pain in calves after walking and muscle weakness. It usually occurs in hands and feet. The most common causes include Diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, certain infections like HIV, Leprosy etc, autoimmune disorder Sjogren’s syndrome, lupus, Guillain-Barre syndrome, certain medications like chemotherapy, Vitamin deficiency especially B vitamins. Treatment includes finding out the cause of the nerve damage and treating it accordingly. Blood glucose control, healthy diet to combat nutritional deficiencies are some examples.
8. Peripheral arterial disease
It is blockage of the vessels which carry blood to legs and feet. This occurs due to certain risk factors like smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, ageing. Due to blockage or narrowing, legs do not receive enough blood supply. Symptoms include pain while walking and relief with rest. In later stages, limb may feel cold along with numbness. There may also be skin color changes along with hair loss. Few steps which can prevent this to happen is avoid smoking, blood sugar control, diet low in saturated fats, regular exercise, maintain blood pressure and cholesterol with in normal range.
9. L5 and S1 nerve root compression (Pinched Nerve)
Sometimes pain in the foot and leg could be due to disc compression in the spine. Specifically, the L5 and S1 nerves when compressed, brings the pain in leg and the foot of affected side. The pain is associated with tingling and numbness. It can significantly affect your walking. On prolonged compression there could be associated weakness as well. Causes of this type of nerve compression could be improper weight lifting technique, poor posture, obesity, not exercising, smoking.
Treatment options
Conservative treatment – which includes rest, anti-inflammatory medications, neuropathic medications, physical therapy
Injection – Getting injection around the nerve as it exits the spinal canal will help in reduction of inflammation and pain. This is done under image guidance ( either fluoroscopy or ultrasound)
Surgery – If the pain continues to persist then last resort is getting the surgery done. It is done in various forms, most common is microdiscectomy.